How Long Can You Keep Your Teeth with Periodontal Disease?
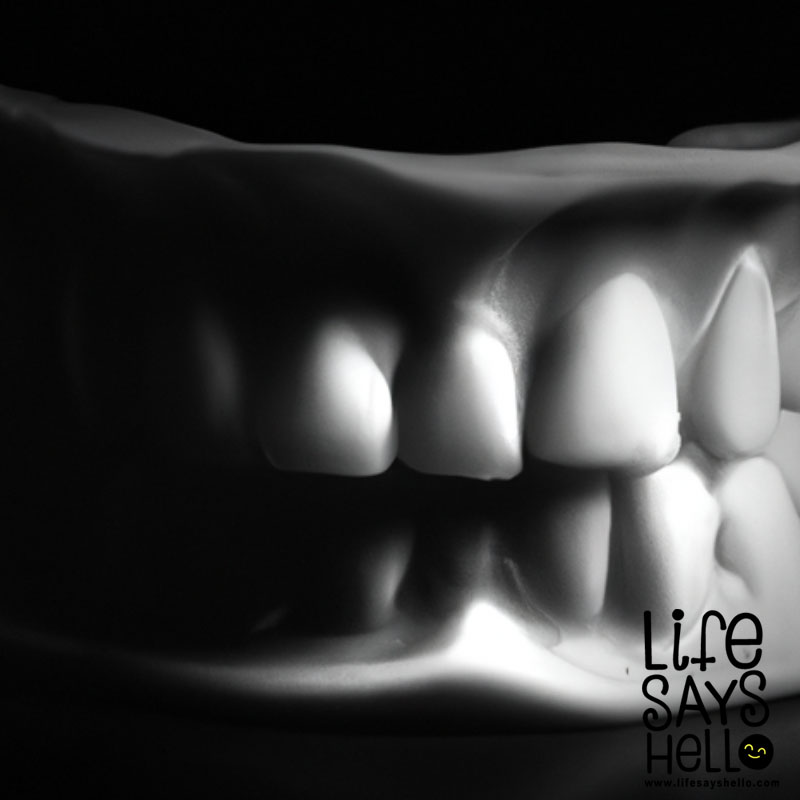
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a serious condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the tissues and bones that support the teeth become inflamed and infected. If left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss and other serious health problems.
In this article, we’ll discuss how long you can keep your teeth with periodontal disease and what you can do to prevent it.
What is periodontal disease?
Periodontal disease is an infection of the tissues and bones that support the teeth. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including poor oral hygiene, genetics, smoking, and certain medical conditions. It starts with the accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth and gums. If not removed, the plaque hardens into tartar, which can only be removed by a dentist or dental hygienist.
Causes of periodontal disease
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of periodontal disease. These include:
- Poor oral hygiene: Not brushing and flossing regularly can allow plaque to build up on the teeth and gums, leading to gum disease.
- Genetics: Some people may be more genetically susceptible to gum disease than others.
- Smoking: Smoking can weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections like gum disease.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are more likely to develop gum disease.
- Medications: Certain medications can affect the health of the gums, making them more susceptible to infection.
Complications of periodontal disease
If left untreated, periodontal disease can lead to several serious health problems. These include:
- Tooth loss: Advanced gum disease can cause the teeth to become loose and eventually fall out.
- Heart disease: Studies have shown a link between gum disease and heart disease.
- Stroke: Gum disease may increase the risk of stroke.
- Pregnancy complications: Pregnant women with gum disease may be more likely to give birth prematurely or have a low birth weight baby.
- Respiratory disease: Gum disease may increase the risk of respiratory disease.
Signs and symptoms of periodontal disease
The signs and symptoms of periodontal disease can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Some common signs and symptoms include:
- Bleeding gums: Gums that bleed when you brush or floss can be a sign of gum disease.
- Bad breath: A persistent bad taste in your mouth or bad breath that won’t go away can be a sign of gum disease.
- Red, swollen, or tender gums: Healthy gums should be pink and firm to the touch. If your gums are red, swollen, or tender, it could be a sign of gum disease.
- Loose teeth: If your teeth feel loose or you notice that they are separating, it could be a sign of gum disease.
- Receding gums: If your gums are pulling away from your teeth, it could be a sign of gum disease.
Diagnosis of periodontal disease
If you suspect you have periodontal disease, it’s important to see a dentist as soon as possible. Your dentist will perform a thorough dental exam and may order X-rays to determine the extent of your gum disease. They may also use a special probe to measure the spaces between your teeth and gums, which can help determine the severity of the disease.
How periodontal disease affects teeth
Periodontal disease can cause significant damage to the teeth and gums. It can weaken the bones and tissues that support the teeth, causing them to become loose or fall out. It can also lead to the development of pockets between the teeth and gums, allowing bacteria to accumulate and cause further damage.
How long can you keep your teeth with periodontal disease?
The answer to this question depends on several factors, including the severity of the disease, how quickly it progresses, and how well it’s treated. In some cases, people with mild to moderate gum disease can keep their teeth for the rest of their lives with proper treatment and maintenance. However, in more severe cases, tooth loss may be inevitable.
Prevention and treatment of periodontal disease
The best way to prevent periodontal disease is to practice good oral hygiene. This includes brushing at least twice a day, flossing at least once a day, and scheduling regular dental checkups and cleanings. If you smoke, quitting can also help reduce your risk of developing gum disease.
If you do develop gum disease, there are several treatment options available. These include:
- Scaling and root planing: This is a deep cleaning procedure that removes plaque and tartar from below the gumline and smooths out rough spots on the roots of the teeth.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics may be prescribed to fight off the infection.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove damaged tissue or to graft healthy tissue onto the gums.
When to see a dentist
If you experience any of the signs or symptoms of periodontal disease, it’s important to see a dentist as soon as possible. Early treatment can help prevent further damage to your teeth and gums and may even prevent tooth loss. Regular dental checkups and cleanings can also help catch gum disease before it becomes a serious problem.
In conclusion, periodontal disease is a serious condition that can lead to tooth loss and other serious health problems. With proper treatment and maintenance, people with mild to moderate gum disease can keep their teeth for the rest of their lives. If you suspect you have gum disease, it’s important to see a dentist as soon as possible to get the treatment you need to protect your teeth and gums.




Comments